Introduction
The Israel-Palestine conflict remains one of the most enduring and devastating crises in modern history, with profound implications for human rights and world peace. The ongoing violence, coupled with shifting global power dynamics—particularly the United States’ reduced involvement in world affairs—has further complicated the path toward resolution. As Israel continues its military bombardments in Gaza and the West Bank, the humanitarian crisis deepens, raising urgent questions about international intervention and the future of the region.
Historical Context: The Roots of the Conflict
The Israel-Palestine conflict dates back to the early 20th century, when tensions between Jewish and Arab communities in British-controlled Palestine escalated. Following World War II and the Holocaust, global support for a Jewish homeland led to the establishment of Israel in 1948, triggering the first Arab-Israeli war. Palestinians, who had lived in the territory for centuries, were displaced in what they call the Nakba (catastrophe), leading to decades of strife.
Subsequent wars (1956, 1967, 1973) and ongoing territorial disputes, including Israeli occupation of Palestinian lands, have fueled violence and resistance. The Oslo Accords (1993–1995) attempted to create a framework for peace, but the process collapsed due to continued settlement expansions, Palestinian uprisings (Intifadas), and political divisions. Today, Gaza remains under an Israeli blockade, and the West Bank faces expanding Israeli settlements, leaving Palestinians with little sovereignty.
Human Rights Violations in the Conflict
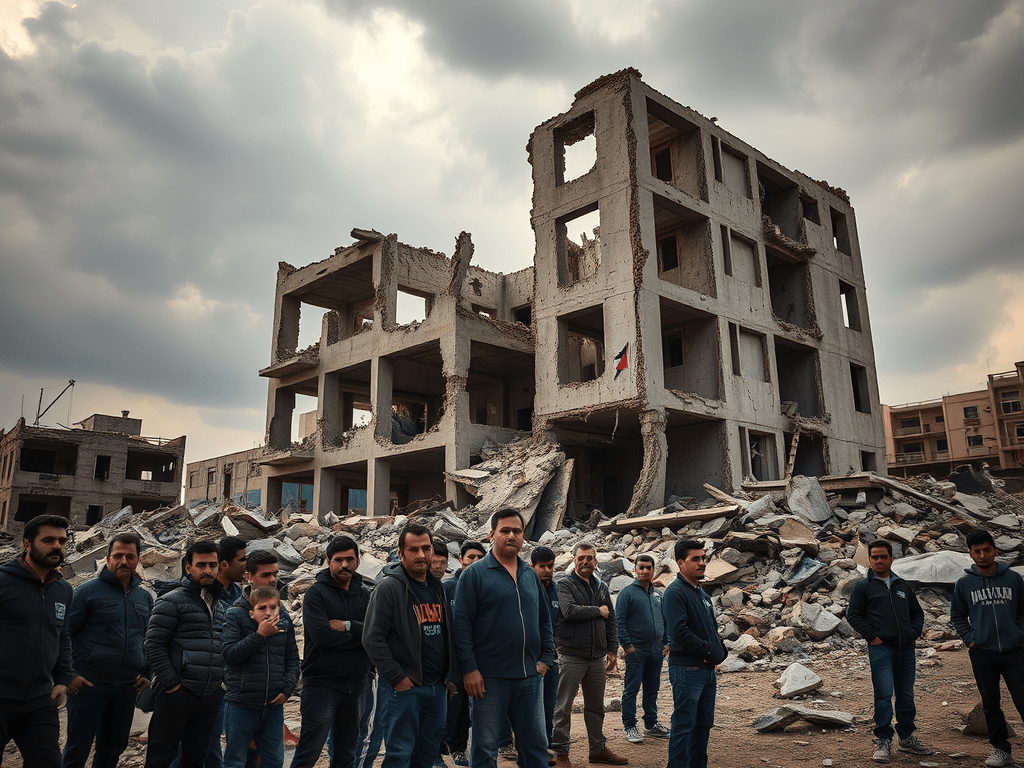
The Israel-Palestine conflict is a stark example of systemic human rights violations. In Gaza, Israeli airstrikes have led to mass civilian casualties, destruction of homes, and severe restrictions on food, water, and medical supplies. The blockade has created what the UN calls an “open-air prison,” with over two million people lacking basic necessities.
On the other hand, Israeli civilians have also suffered from rocket attacks and acts of terrorism by militant groups like Hamas. However, the disproportionate use of force by Israel and the lack of accountability for civilian deaths have drawn widespread criticism from human rights organizations. Reports from groups like Amnesty International and Human Rights Watch have labeled Israeli actions as apartheid, citing discriminatory laws and policies against Palestinians.
The U.S. Withdrawal and Its Global Implications
For decades, the United States has played a central role in mediating the Israel-Palestine conflict. However, recent shifts in global power have seen the U.S. take a backseat in world affairs, with other actors—such as China, Russia, and regional powers like Iran and Turkey—filling the void.
Without strong U.S. mediation, several key consequences emerge:
- Escalation of Military Action – Israel may feel emboldened to continue military operations without fear of U.S. intervention, leading to prolonged conflict and more civilian casualties.
- Humanitarian Crisis Worsens – The lack of international pressure could further restrict humanitarian aid, worsening living conditions in Gaza and the West Bank.
- Emerging Geopolitical Players – China and Russia may increase their diplomatic influence, reshaping Middle East politics in unpredictable ways.
- Regional Instability – With Iran’s growing involvement and increased activity from militant groups, the conflict could escalate into a broader regional war, drawing in countries like Lebanon and Syria.
Impact on World Peace and Stability
The ongoing conflict has far-reaching consequences beyond the Middle East. It fuels extremism, increases refugee crises, and exacerbates divisions in global politics. The international community’s failure to address Palestinian suffering undermines the credibility of human rights institutions and creates a precedent where military power overshadows justice.
Furthermore, instability in the region affects global economic and energy markets. Rising tensions can lead to oil price fluctuations, disrupt trade routes, and contribute to economic downturns worldwide.
The Path Forward: A Call for Justice and Diplomacy
For lasting peace, a renewed commitment to diplomacy, human rights, and international law is essential. A two-state solution remains the most widely supported path, but it requires genuine political will from global powers, including the U.S., the EU, and Middle Eastern nations. Key steps include:
- Ending the blockade on Gaza to allow humanitarian aid and reconstruction.
- Halt Israeli settlement expansion in the West Bank to preserve the possibility of a Palestinian state.
- Promoting accountability through international legal mechanisms to address war crimes on both sides.
- Encouraging regional cooperation with Arab states playing a more active role in mediation.
Conclusion
The Israel-Palestine conflict remains a profound test of human rights and global governance. The world’s failure to act decisively continues to fuel suffering, deepen regional instability, and threaten global peace. As the U.S. steps back from its traditional leadership role, the need for a balanced, just, and sustainable resolution has never been more urgent. Only through a commitment to diplomacy, justice, and humanitarian aid can the cycle of violence be broken and peace achieved.